The world's first all-soft robot octobot
The TechnologyReview website published an article in which Harvard researchers used a clever method to create an octopus-like robot that was not only fully software but also moved automatically. The following is the original content:
This robot is called octobot (octopus robot), small and soft, and can be placed in the palm of your hand. It looks like the new exotic product that kids use at birthday parties. But don't look at the small size of the octobot, which is not surprising, but it represents a big step forward in robotics.
Harvard researchers say it is the first fully self-sufficient all-software robot: no electronic hardware (battery or computer chip), and it doesn't need to be connected to a computer to move.
Otcobot is actually a pneumatic robot. To make it move, the researchers pumped the hydrogen peroxide liquid into two reservoirs in the robot's body. The pressure pushes the liquid through the tube inside the robot and eventually encounters a platinum wire. The platinum wire catalyzes the reaction and produces a gas. The gas expands and moves into a small chip called a "microfluidic controller." It first introduces the gas into the touch of the robot's half, and then introduces it into the other half of the hand, alternating iteratively.
By alternately releasing the gas in this way, the octopus robot looks like it is dancing, constantly swinging the tentacle and starting to move. One milliliter of fuel can move it for about eight minutes.
So how do you make such a robot? “All the parts need to be made by ourselves,†says Ryan Truby, a graduate student at the lab. The molds and microfluidic chips used to make the Octobot form were developed in the next-door laboratory.
As for the materials used to make octobot, most microfluidic laboratories are readily available. But the researchers made 300 attempts to find the right formula. First they placed a microfluidic chip in an empty, custom octopus mold. The silicone mixture is then poured into a mold to encase the chip. They then used a 3D printer to inject different ink lines into the silicone, then baked it for four days, allowing the robot to set and evaporate some of the ink lines, leaving a conduit for compressed gas to pass through.
With sensors and programmability, researchers can better control the motion of the robot. But the octobot is just a minimalist robot, the purpose is to prove that such a software robot can be made.
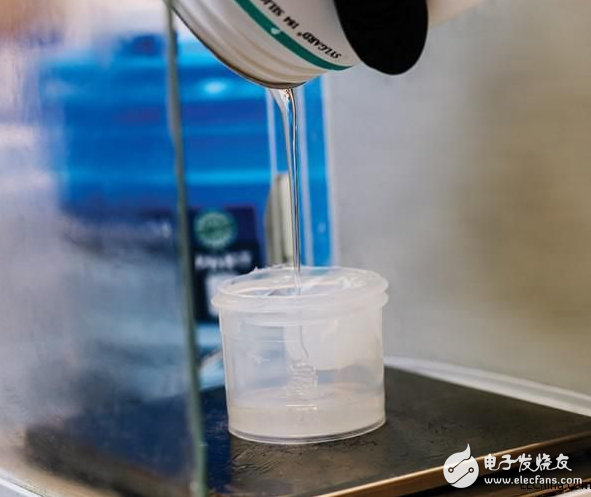

The researchers were measuring the silicone mixture and the body of the octobot was made with it.

Prepare platinum ink for use with 3D printers.

Use such a mold to make a unique shape of the robot.
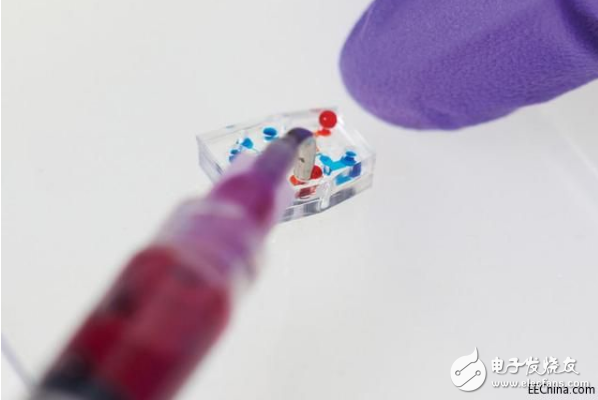
The main component of Octobot is the soft microfluidic chip, which is the "brain" of the robot, which directs the movement of eight tentacles.
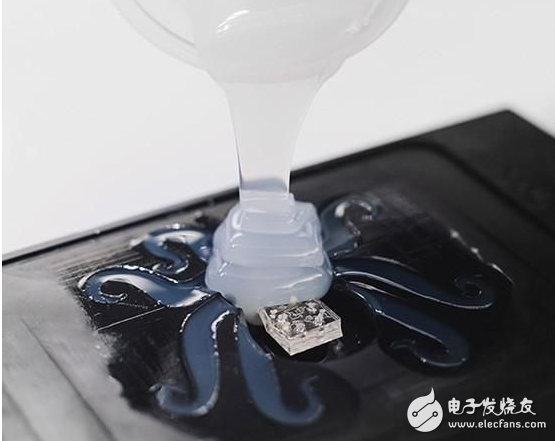

The first step in assembly is to cast the silicone mixture into the mold.
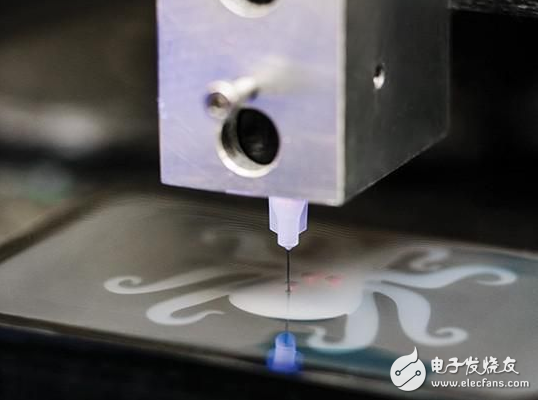
Next, the ink line was extruded into the silicone body using a 3D printer. Platinum ink can turn liquid hydrogen peroxide into a gas to move the tentacle; the other ink then evaporates to form a gas passage throughout the robot.
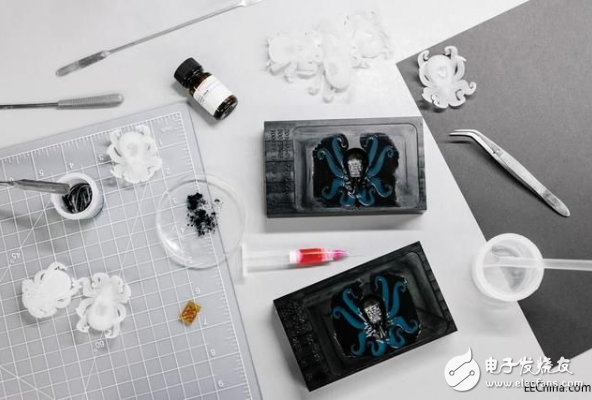

The full set of tools and molds that researchers use to create robots. They made a total of 300 attempts.

Close up of a microfluidic chip inside the robot.
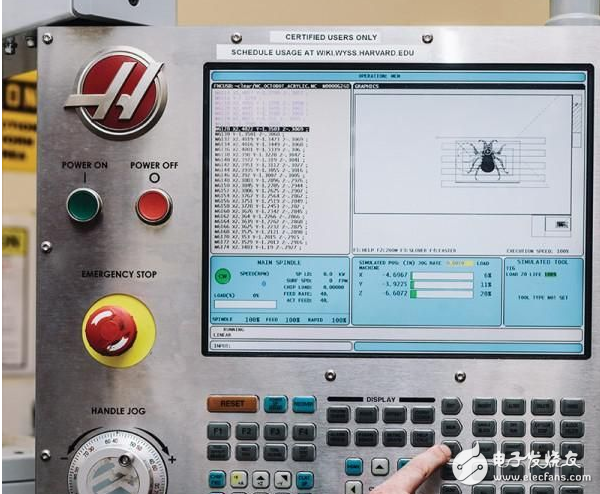

The mill is used to make octobot molds.
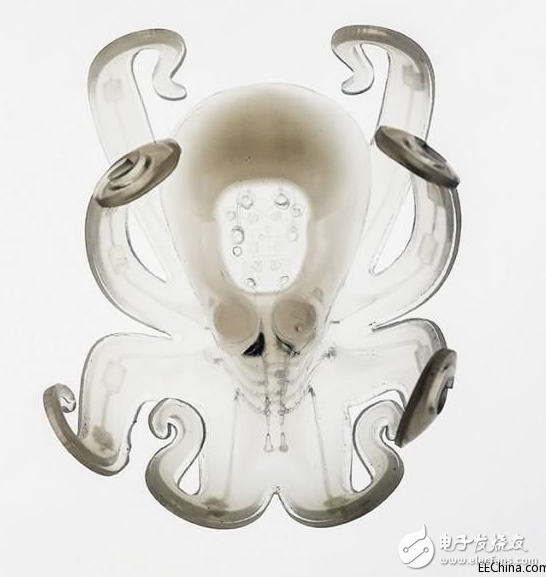
The octobot is usually colorless. Flash dyes are sometimes added for a clearer display.
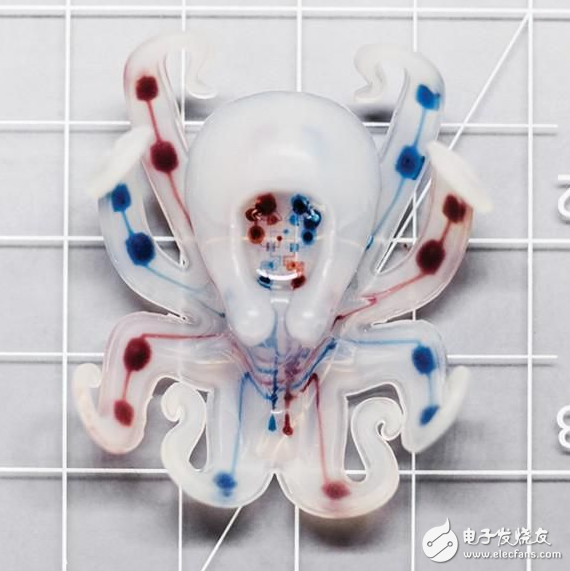
The color indicates that the gas can pass through the robot body through different passages, alternately moving half of the tentacle and let it swing. This robot is about two inches long, about 5 centimeters
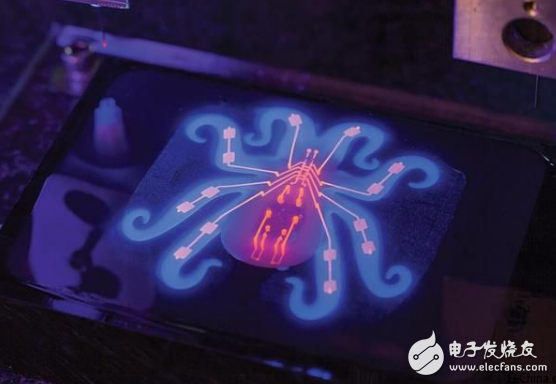
The ink can shine under black light, and this function is purely fun.
Ptfe Gasket Pressure Rating,Ptfe Gasket Sheet Specification,Ptfe Gasket Temperature Range,Expanded Ptfe Gasket Tape
Cixi Congfeng Fluorine Plastic Co.,Ltd , https://www.cfptfeseal.com