With June 16th, the NB-IoT (Narrowband Cellular Internet of Things) standard was approved by the international organization 3GPP, and there is no doubt that 2016 will be included in the history of communication as the NB-IoT commercial first year. Just as the mobile Internet is eager for the 4G era in the past decade, today's Internet of Things is also eager for a strong cellular IoT infrastructure network, and NB-IoT is undoubtedly the best choice for this basic network.
At the M2M conference in London in April this year, Huawei demonstrated the NB-IoT (narrowband cellular Internet of Things) strategy and innovations in IoT applications and smart cities, and introduced the cooperation with partners to build the NB-IoT ecosystem. Work, including the establishment of the Vodafone NB-IoT Open Lab with Vodafone in Newbury, UK, aims to leverage the potential of NB-IoT to create social and economic benefits.

Figure 1: Vodafone and Huawei celebrate the establishment of a narrow-band IoT open laboratory
From a business perspective, cellular networks currently cover 90% of the world's population, covering more than 50% of geographic locations. Based on the existing cellular network, operators can provide a very competitive IoT technology, namely NB-IoT. On April 25th, British operators Vodafone and Huawei announced the launch of the new NB-IoT laboratory in Berkshire, where Vodafone UK headquarters is located, which has a major impact on the development of NB-IoT technology.
Huawei and Vodafone jointly established the Vodafone NB-IoT Open Lab to help partners with network solution validation, new application innovation, device integration, business model research and product compliance verification, thereby accelerating the vertical industry application process. Promote the development of the industrial chain.
NB-IoT is built on a cellular network and consumes only about 180KHz. It can be deployed directly on GSM networks, UMTS networks or LTE networks to reduce deployment costs and achieve smooth upgrades.
NB-IoT technology is an LPWA (Low Power WAN) solution defined by the 3GPP standard with the following advantages:
1. Massive connection: Up to 100,000 connections per cell; NB-IoT has 50-100 times higher uplink capacity than 2G/3G/4G, which means that in the case of the same base station, NB-IoT can be compared Existing wireless technologies provide 50 to 100 times the number of accesses.
2. Ultra low power consumption: battery life is up to ten years;
Low-power features are an important indicator for IoT applications, especially for devices and occasions where batteries cannot be replaced frequently, such as sensors that are placed in remote areas of the Alpine Wilderness. The battery life of several years is the most essential requirement. In the absence of breakthroughs in battery technology, battery power can only be extended by reducing device power consumption. The energy consumed by a communication device is often related to the amount or rate of data, that is, the size of the data packet sent per unit time determines the amount of power consumption. The amount of data is small, and the modem and amplifier of the device can be adjusted to a very small level. NB-IoT focuses on small data volume and small rate applications, so the power consumption of NB-IoT devices can be very small, which can guarantee the battery life of more than 5 years.
3. Deep coverage: can achieve 20db higher coverage gain than GSM;
NB-IoT boosts 20dB gain over LTE, which is equivalent to a 100x increase in transmit power, which means a 100x increase in coverage, even in areas such as underground garages, basements, and underground pipes that are difficult to reach.
4. Security: Inherit 4G network security capabilities, support two-way authentication and strict air interface encryption to ensure the security of user data;
5. Stable and reliable: Provides carrier-grade reliability access, effectively supporting IoT applications and smart city solutions.
NB-IoT can be directly deployed on GSM network, UMTS network or LTE network, and can be reused with existing network base stations to reduce deployment cost and achieve smooth upgrade. However, using a separate 180KHz band does not occupy the voice and data bandwidth of the existing network. To ensure that traditional business and future IoT business can be carried out stably and reliably at the same time. Taking the smart meter reading application as an example, compared with the use of wired PLC meter reading data recovery success rate of about 60%, NB-IoT can ensure the data recovery rate is 99%, and the reliability is greatly improved.
6. Low cost
Low speed, low power and low bandwidth bring low cost advantages. Low rate does not require large buffers, so it can be cached small, DSP configuration is low; low power consumption means low RF design requirements, small PA can be achieved; because of low bandwidth, do not need complex equalization algorithms. These factors make the NB-IoT chip very small. The cost of the chip is often related to the chip size. The smaller the size, the lower the cost, and the lower the cost of the module.
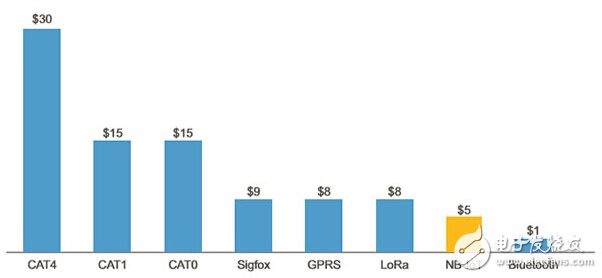
Figure: Cost comparison of various wireless modules
Long-distance communication technology NB-IoT is a revolutionary technology. It is a narrowband Internet of Things technology based on cellular networks defined by Huawei and defined by 3GPP. It supports massive connectivity, deep coverage, and low power consumption. These inherent advantages make it ideal for IoT applications such as sensing, metering, and monitoring. It is suitable for smart meter reading, intelligent parking, vehicle tracking, and logistics. Monitoring, intelligent agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery, as well as smart wear, smart families, smart communities and so on. The demand for wide coverage, low power consumption, and low cost in these areas is very clear, and the widely used 2G/3G/4G and other wireless technologies cannot meet these challenges.
The cellular Internet of Things has important strategic significance and broad development prospects, and mainstream operators around the world are incorporating it into the entire company's strategic system. In the past 2015, a number of mainstream operators including China, South Korea, Europe, the Middle East and North America have launched pilots based on pre-standard NB-IoT technology and launched end-to-end technology and business verification. A number of mainstream operators, including Vodafone and China Mobile, also expressed their intention to start building the NB-IoT commercial network as soon as possible. On the other hand, many operators including Europe and South Korea encountered LoRa and Sigfox. The strong competitive pressure will also accelerate the construction of the NB-IoT network.
As the profits of traditional telecom services become thinner and thinner, the entire telecom industry is looking for new profit growth points, and the Internet of Things, which is the closest to the operators' business and has a huge market prospect, will undoubtedly become the best market entry for operators.
Fan And Filter,Panel Fan Filter,Cabinet Fan Filter,Fan Filter Dustproof
Wonke Electric CO.,Ltd. , https://www.wkdq-electric.com