The modern stadium not only absorbs the latest developments of contemporary architectural art and the essence of local humanistic history, but also creates a stadium building that conforms to the contemporary spirit, and all kinds of sports soft and hardware facilities must be perfected. Of course, there must be good Lighting environment.
Lighting relies on the function of light to properly illuminate and act on the visuals of athletes, referees, and spectators. Allowing athletes to concentrate on giving full play to their level of competition and creating good results; enabling the referee to quickly make accurate judgments; allowing the audience to easily appreciate the athlete's technical movements and feel the fierceness of the venue A lively competitive atmosphere; the picture of the color TV broadcast is clear and vivid. Therefore, a good lighting environment occupies an important position and role in modern stadiums. For this reason, the following three principles must be mastered in the construction of stadium lighting:
(1) to meet the visual requirements of the athletes during the competition, so that the objective impact of the lights on the competition is minimized;
(2) to meet the visual requirements of the audience, so that the feeling of discomfort caused by the lighting when watching the game is minimized;
(3) Meet the lighting requirements of color TV broadcast and improve the quality of broadcast.
1. Stadium lighting design standards
The comprehensive stadium competitions are mainly track and field, football, etc. The design standards for venue lighting are as follows:
(1) Guide to artificial lighting in football fields: FIFA. The standard includes competition grading, lighting requirements, lighting parameter recommendation values, site lighting measurement, etc. It is the most comprehensive and latest standard for artificial lighting in football stadiums. The standard was applied in the 2002 Korea-Japan World Cup.
(2) Manual lighting guide for multi-purpose indoor stadiums: International Federation of Athletics (GAISF), European Broadcasting Union (EBU). The standard introduced the High Definition Color Television Broadcast (HDTV) clause for the first time, and the lighting standard has taken another step. However, HDTV is still in the development stage, so the requirements are based on the knowledge and experience available at the time of standard compilation; compared to other standards and specifications, HDTV also requires an emergency system to provide minimal emergency TV lighting. .
(3) Lighting guide for sports with color television broadcast and film system: Document No. 83 of the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). The CIE83 technical document focuses on the requirements for color television camera lighting, and also explains the differences between TV camera and film camera requirements.
(4) Guide to the determination of luminosity regulations for sports lighting devices: Document No. 67 of the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). In 1986, the CIE4.4 Committee of the International Commission on Illumination developed the technical document CIE67. The purpose of this report is to develop standard procedures for the calculation, measurement and illumination characteristics reporting of indoor and outdoor sports lighting.
(5) Football field lighting: Document No. 57 of the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). In l983, the International Commission on Illumination officially promulgated the "Lighting for footbal1", the technical document of CIE57. This standard is a guideline for floodlighting in football fields. It is suitable for training grounds to sports with stands.
(6) Civil building lighting design standards: GBJ133-90. It will be implemented from December 1, 2004.
(7) Electrical design specifications for civil buildings: JGJ/T16-92. Implemented on August 1, 1993.
(8) Sports building design specification: JGJ31—2003J265—2003). This specification is an industry standard jointly promulgated by the Ministry of Construction and the State Sports General Administration. It will be implemented from October 1, 2003. This standard is the first professional standard for sports architecture in China.
Which of the above criteria is used for site lighting depends on the positioning of the constructor's functional requirements, ie the nature and level of the competition. The International Federation of Athletics (GAISF) is classified according to the level of competition, either professional or amateur, and FIFA is classified according to whether there is a TV broadcast.
Generally speaking, the standards set by international sports organizations are higher than and better than those of China's national and industry standards. Therefore, the construction of sports grounds is purely used for domestic competition and training, and can follow the above (6), (7), (8). The criteria are based on the standard, and other standards are supplemented. If it is an intercontinental or international competition venue, it must be designed in accordance with the principles of (1) to (5) and other supplements.
The core content of lighting standards are illumination standards and lighting quality standards. Lighting quality standards include glare, light source color temperature, color rendering index, light directionality, green and energy saving requirements.
2. Sports ground lighting design mode
In the past, the design unit was based on the design work book of the construction party, and fully designed the lighting system (including calculation, plan determination, equipment and control system selection, and even construction instructions, etc.), and then the construction party entrusted the electromechanical installation unit to construct according to the map. Installation, commissioning and delivery. This mode of operation, which applies to the construction process of the past planned economy era, is now largely unworkable.
Nowadays, the more common practice is to design the architectural plan by the architectural design unit. The building electrical designer determines the design and design standards of the site lighting, and then deepens the design by the professional lighting design unit. This requires the building electrical designer to design. In the process of site lighting system, we must first understand the relevant design specifications and standards, and then according to the function of the venue, the level of the venue, the scale of the sports competition or the scale of various activities will be held after the completion. The technical status of the stage lighting system equipment can be comprehensively analyzed, and finally the design standard and system plan of the site lighting system are determined.
This mode of operation brings significant benefits:
The construction procedure is standardized and clarified, which not only conforms to the national bidding regulations, but also conducive to the standard construction of the project, and plays a certain protective role for investment; the division of work is clear, and the duplication of design, redundant calculation and CAD drawing work is appropriately reduced. Through the bidding of lighting integrators, lighting lighting control equipment can be selected from well-known brands at home and abroad, with excellent price, strong project implementation capability, high quality of service and high reputation, to ensure the comprehensiveness of the project. Quality; through the evaluation of bidding, the project investment is clear and gradually reasonable; after the project is completed and put into operation, the after-sales service of the integrator can be implemented.
3. Arrangement and installation of stadium lighting design
Whether the arrangement of the lamps is reasonable or not directly affects the effect and economy of the site lighting. The lighting methods commonly used in sports buildings are mainly in the following ways: outdoor sports grounds, light poles, four towers, multi-towers, light belts, light belts and lighthouses; indoor sports venues, Uniform (Starry), light belt (over the field and over the field), hybrid.
3.1 Four tower layout
Until today, the lighting facilities of most stadiums in the past were four-tower layouts. If we have some shortcomings (such as different visual orientation changes and effective blunt shadows), it is not demanding. Then you can still meet the basic requirements. Four lighthouses are set at the four corners of the site. The tower height is generally 25 to 50 m, and narrow beam lamps are commonly used. This arrangement is suitable for soccer fields without runways, low lighting utilization, difficult maintenance and repair, and high cost. If the quality of the lighting is not excessively demanding, it can meet the general requirements of athletes and audiences. The proper location of the lighthouse creates a suitable illumination distribution on the field by using a variety of different beam angle projections. But today, movies and televisions require high and uniform vertical illumination, requiring that the angle of light incident on the farther portion of the field is much less than the prescribed limit. The effect of the higher brightness obtained with large gas discharge lamps, combined with the traditional tower height, inevitably produces excessive glare. The shortcoming of this four-tower lamp form is that the visual changes in different viewing directions are larger and the shadows are deeper. From the color TV broadcast, it is more difficult to control the vertical illumination in all directions and to control the glare. In order to meet the Ev/Eh 44 value requirement and less glare, it is necessary to take some improvement measures for the four-tower lighting method:
(1) Move the four tower positions to the sides and the side lines, so that the opposite side of the field and the four corners can obtain a certain vertical illumination;
(2) increase the number of floodlights on the lighthouse on the side of the main camera of the TV to enhance the beam projection;
(3) Supplement the light strip illumination on the top of the viewing platform on the side of the main camera of the TV. Pay attention to controlling the glare and should not make the audience at both ends of the venue aware.
3.2 Multi-tower layout
This type of lamp is used to set up a group of lighthouses (or light poles) on both sides of the site, suitable for practice sites such as football, volleyball, tennis courts, etc. Its outstanding advantage is that the electricity consumption is relatively low, and the vertical illumination and the horizontal illumination are better. Due to the low pole, this arrangement has the advantages of low investment and convenient maintenance.
The poles should be evenly arranged, and 6 towers or 8 towers can be arranged. The height of the poles should not be lower than 12 m, the projection angle should be between 150 and 250, and the projection angle to the sideline of the site should not exceed 750 at most, and the minimum is not less than 450. Generally, the medium beam and the wide beam floodlight are used. If there is a spectator stand, the aiming point layout work is very detailed. The disadvantage of this type of cloth is that when the pole is placed between the field and the auditorium, it is more difficult to obscure the viewer's line of sight to eliminate the shadow. In the football field without television broadcast, the lateral arrangement lighting device adopts multi-tower arrangement, and does not adopt the optical belt arrangement. The lighthouse is usually placed on both sides of the stadium. In general, the height of the lighthouse of the multi-tower light can be lower than that of the four corners. The multi-tower is arranged with four towers, six towers and eight towers. In order to avoid the line-of-sight interference of the goalkeeper, the midpoint of the goal line is used as the reference point, and the lighthouse cannot be arranged within at least 10 m on both sides of the bottom line.
The height of the lighthouse of the multi-tower light is calculated. The triangle is calculated perpendicular to the course, parallel to the bottom line, ≥250, and the height of the lighthouse is h≥15m.
3.3 Optical belt layout
The lamps are arranged in rows on both sides of the court to form a continuous light strip illumination system. Its illumination uniformity, the brightness between the athlete and the stadium is better. At present, this kind of lighting method is recognized in the world, which can meet various requirements for color television broadcasting. The length of the light belt is more than 10m above the goal line (for example, the sports field with the runway, the length of the light belt is preferably not less than 180m) to ensure that the goal area has sufficient vertical illumination from the back. At this point, the projection angle can be reduced to about 200. If a low-brightness illuminator is used, it can be further reduced to about 150. Some stadium lights are very close to the sideline of the venue (the angle is above 650), and the vertical edge of the venue can not be obtained, so it is necessary to add "retracted" supplementary lighting.
In general, the optical strip layout uses a combination of several different beam angles for projection, a narrow beam for long shots and a medium beam for near projection. Disadvantages of the optical belt arrangement: The technique for controlling glare is strict, and the object entity feels slightly worse.
3.4 Mixed layout
The hybrid arrangement is a new type of lighting method that combines a four- or multi-tower arrangement with an optical belt arrangement. It is currently a large-scale integrated stadium in the world to solve the lighting technology and lighting effect is a better form of cloth lighting. The mixed arrangement absorbs the advantages of the two types of lamps to enhance the sense of solidity, and the vertical illumination and uniformity in the four directions are more reasonable, but the degree of glare is increased. At this time, the four towers are often not set up independently, but are combined with the buildings, so the cost is relatively low.
The four-column floodlights are mostly narrow beams, which solve the long-range shot; the light belts are mostly medium beams, which solve the near-projection. Due to the mixed arrangement, the projection angle and azimuth arrangement of the four towers can be flexibly processed, the length of the light strip arrangement can be appropriately shortened, and the height of the light strip can be appropriately reduced.
3.5 Civil engineering treatment and installation
The civil works of the stadium are closely related to the entire lighting scheme. When there is no shed or lack of arranging in the audience, it is necessary to consider the use of a separate light bridge. Whether or not to use the four tower lights, the urban planning department must also be consulted, and the four-tower and multi-tower lighting forms are closely related to the overall artistic effect of the building. Whether using four-tower, multi-tower, light-belt or hybrid layout, the installation, maintenance and overhaul of the luminaires must be considered at the selection stage.
At present, many stadiums in the world use lighthouses, mostly three steel pipes or multiple steel pipe combination lighthouses, as well as variable-section reinforced concrete and inclined reinforced concrete lighthouses.
The following are some issues to be noted in the installation and treatment of the lighthouse and the light belt.
3.5.1 Civil construction of the lighthouse
(1) The area of ​​the light stand on the lighthouse is related to the form and quantity of the light cast, but there should be room for free choice in the processing of the shape and proportion of the light stand. The area of ​​the lamp stand should be margined for future expansion.
(2) Although the height of the lighthouse must obey the functional requirements, the structure is reasonable, and the construction conditions and local climatic conditions must be carefully considered.
(3) Maintenance and maintenance conditions are extremely important. It is necessary to consider using an elevator for maintenance or to lower the entire lamp holder to the ground for maintenance.
(4) In coastal areas and areas with salt spray corrosion, salt-proof reinforced concrete beacons should be preferred to avoid exposed steel structure.
(5) There are three situations in which a lighthouse has a relationship with a building:
a When the lighthouse is independent of the building, the structural basis is well treated, but the projection distance is relatively long;
b When the lighthouse is attached to a building, the structural basis needs to be treated separately. But the lighthouse tower is connected to the building;
c The lighthouse is attached to the overall combination of the building and can handle aesthetic problems well. The possibility of adopting this scheme should be given priority.
3.5.2 Civil Engineering of Light Belt
(1) The light strip is generally arranged in one or two layers of light-emitting luminaires. If the arrangement is difficult, the rear-reduced light strip should be used as a supplement.
(2) The dimensions of the light strips on both sides are not necessarily consistent with the size or height of the center of the field, but the angles projected to the center of the field should preferably be approximately equal.
(3) The light belt is generally located on the light bridge. The size of the maintenance horse track (also called the maintenance corridor) should not be less than 1.5m × 2m (width X height). It is best to pass around and be rainproof. Sun protection, ground insulation.
(4) There are two situations in the relationship between light belt and building:
a Use the shed to set up the light belt, the height of the shed should be able to meet the functional requirements; the current light belt should be placed under the shed as much as possible, not at the top of the shed.
b Set the light strip independently. In the absence of a pick-up, if the highest row of viewers is reasonable in height and distance, a light strip can be placed on the back of the auditorium, and the light strips are placed on separate light bridges. The light bridge layout can be more flexible, but the relative cost is higher.
This kind of light stand should be considered together with the civil works. Some stadiums are often on one side, but there is a shed, and there is no shed on one side. For example, the light belt scheme is used to set up an independent light bridge.
This site statement: This article is published for the purpose of transmitting more information, its authenticity has not been confirmed. Reprint please indicate the source!

BeCu finger strips can be used for closing a gap between two surface and provide the high EMI shielding effectiveness in enclosure applications where extremely low closure forces are required. The beryllium finger stock gasket have high resistance to stress relaxation, and good corrosion resistance. They can be plated with many choice of metal finished to ensure their compatibility with any mating surface. They will not burn when affected by radiation.Then the designers of computers and electronics consumers regard it as an ideal product for EMI shielding over a broad frequency range.
Features/Advantages:
Excellent electrical and RF conductivity
High tensile strength
High shielding effectiveness
Superb anti-Corrosion
Longevity
Easy installation
Cost effective
Numerous plating options
Excellent performance at high temperature
Moisture and UV resistant
Attachment methods:
Clip on
Conductive adhesive
Soldring
Riveting


Shielding effectiveness(25% compression)
Magnet field
Electric field
Flat wave
Standard finger strip
100dB
100dB
90dB
Soft finger strip
95dB
85dB
75dB
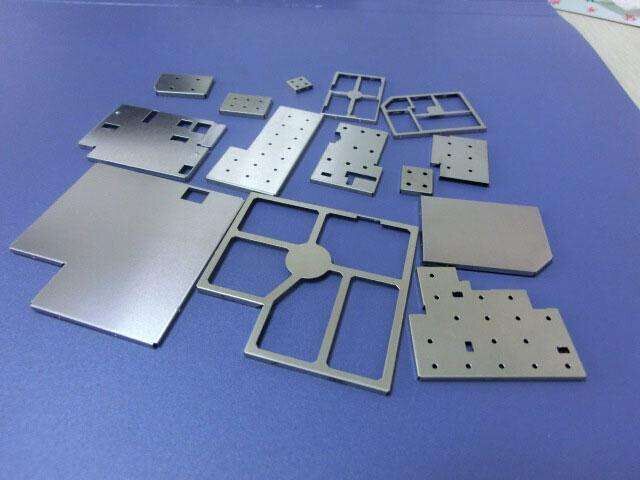

EMI shielding case
,shielding cover ,shielding can, shielding box
Material
carbon
steel; spring steel; alloy steel; stainless steel;nickel steel;music
steel,etc
Surface
treatment
Zinc,
Nickel, Silver, Golden, Tin, Powder, Coating,etc
Quality
Control
100%
inspection before packing or shipment
Application
Automotive,
medical device, electronics, toy ,etc.
Beryllium Copper Gasket
Beryllium Copper Gasket,Beryllium Copper Metal Gasket,Beryllium Copper Finger Stock Gasket,Beryllium Copper Emi Shielding Gasket
JINAN EMI SHIELDING TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. , http://www.emirfi.com